Road Health allowing effective road maintenance strategies

In a recent project conducted with a major road network, our product Road Health showcased its remarkable effectiveness by identifying several sections requiring maintenance. This project aimed to compare NIRA's innovative approach with traditional methods, highlighting the advantages of using real-time, connected vehicle data for road condition monitoring.
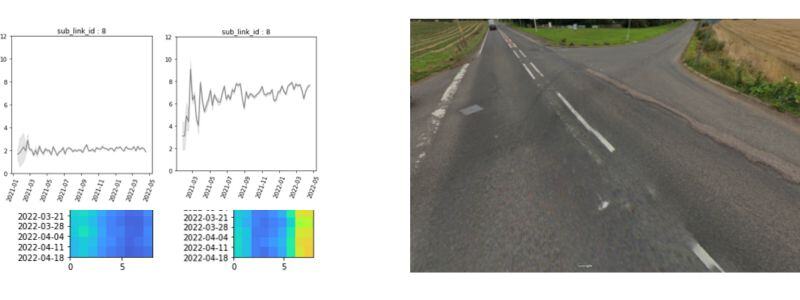
Visualization - The provided image illustrates the data input received, showcasing graphs displaying the variation of the International Roughness Index (IRI) over time. One lane exhibits a degradation in road quality, while the other remains unaffected. Through connected vehicle data, customers gain the ability to track these changes and pinpoint the most critical areas within the road network.
Key Outcomes of the Trial
Identification of Critical Maintenance Areas: The Road Health system's capability to continuously display current International Roughness Index (IRI) values and track changes over time was pivotal. It allowed for precise monitoring of specific areas that were previously overlooked by traditional inspection methods. For instance, the system successfully identified a critical section that had been missed in routine surveys, leading to its immediate inclusion in the maintenance program.
Enhanced Monitoring and Maintenance Planning: The system enabled ongoing, real-time assessment of road conditions across the entire network. This dynamic monitoring meant that maintenance teams could respond promptly to emerging issues, rather than relying solely on periodic inspections. The continual data stream provided a much more detailed and current understanding of road conditions, ensuring that maintenance could be carried out more effectively and efficiently.
Integration with Geographical Positioning Systems: By integrating our road condition data with geographical positioning systems, the Road Health solution provided highly detailed and accurate mapping of road conditions. This integration facilitated easier and faster assessments by maintenance teams. The GPS-based mapping allowed for precise localization of problem areas, enabling targeted maintenance that reduced unnecessary work and focused efforts on the most critical sections.
Supporting Strategic Decision Making: The trial also demonstrated how the system's dashboard and graphical user interface (GUI) could support strategic decision-making. Maintenance managers could easily visualize the state of the entire network, analyze trends over time, and prioritize interventions based on the severity and urgency of issues identified by the system. This data-driven approach ensured that resources were allocated where they were most needed, improving the overall efficiency of the maintenance operations.
Proactive Maintenance and Cost Savings: The trial underscored the cost-effectiveness of the Road Health system. By using existing vehicle sensors to gather data, the solution eliminated the need for additional hardware, significantly reducing implementation costs. Furthermore, the ability to identify maintenance needs proactively helped prevent the deterioration of road conditions, thereby reducing the frequency and cost of major repairs.
Conclusion
The trial's success highlighted the potential of Road Health in modernizing road maintenance practices. By moving away from traditional, periodic assessments to a continuous, real-time monitoring approach, road authorities can enhance safety, optimize resource allocation, and achieve substantial cost savings. This project exemplifies how innovative technologies can lead to smarter, more effective road maintenance strategies, ultimately contributing to safer and more reliable road networks.




